PEFT (Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning) & LoRA (Low Rank Adaptation)
LoRA Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685
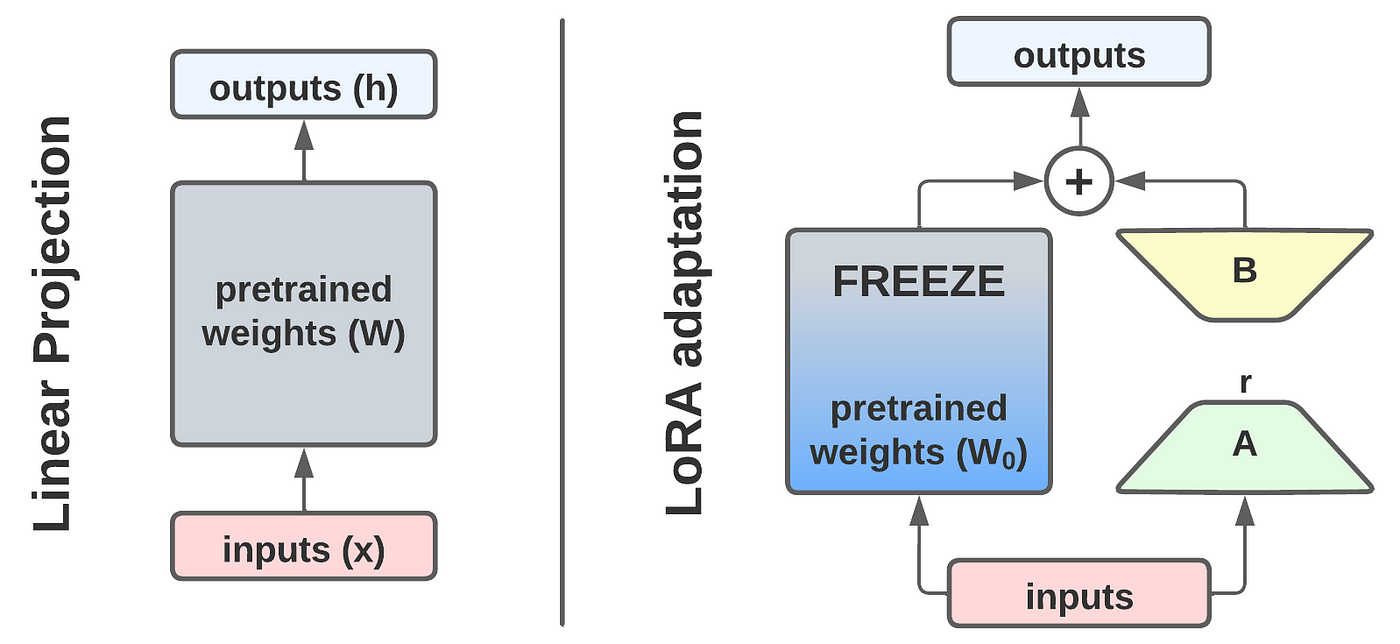
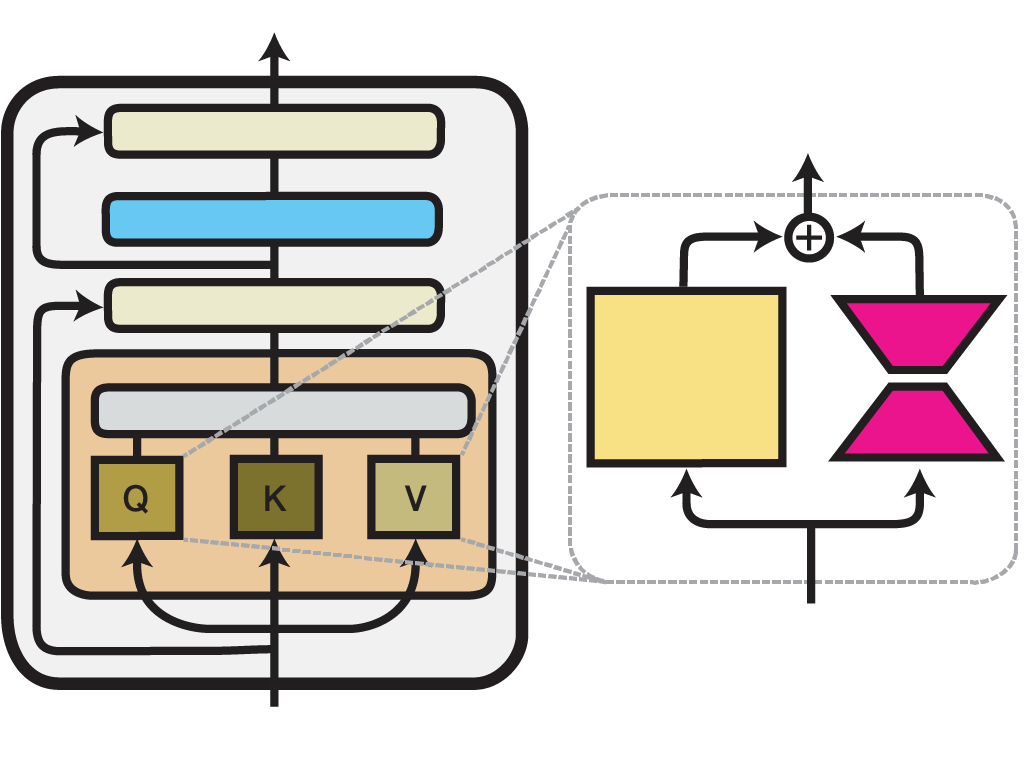
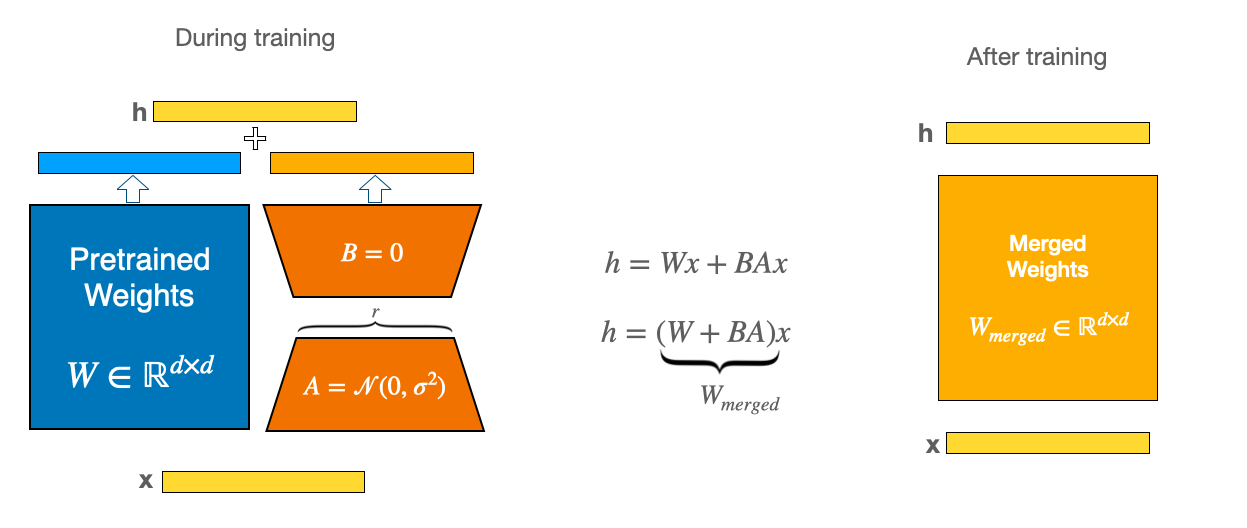
SVD (Singular Value Decomposition)
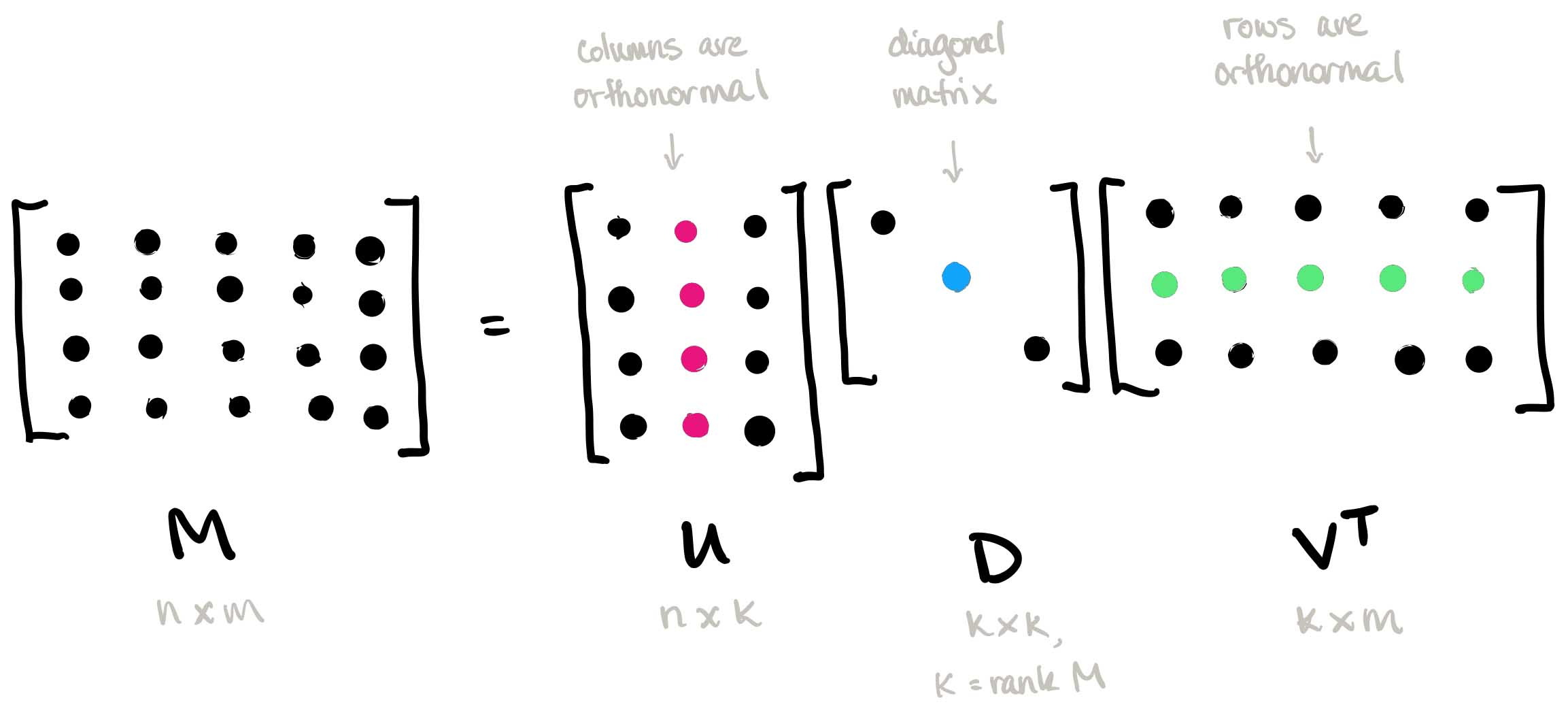
Image Compression with SVD: https://timbaumann.info/svd-image-compression-demo/
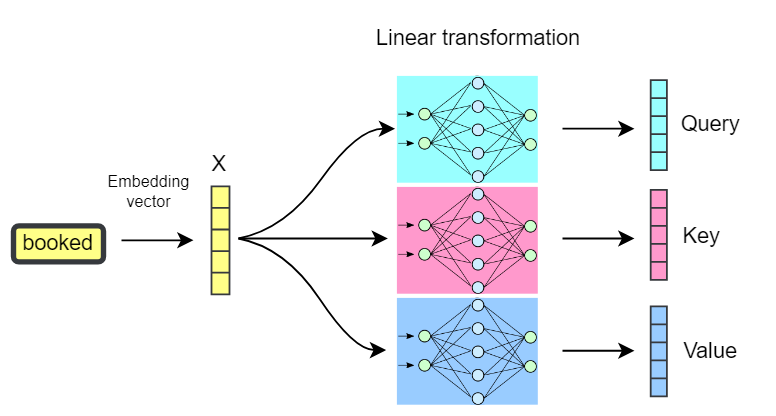
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
...
...
queries = rearrange(
self.query(x),
rearrange_heads,
num_head = self.num_heads
)
keys = rearrange(
self.key(x),
rearrange_heads,
num_head = self.num_heads
)
values = rearrange(
self.key(x),
rearrange_heads,
num_head = self.num_heads
)
...
out = self.projection(out)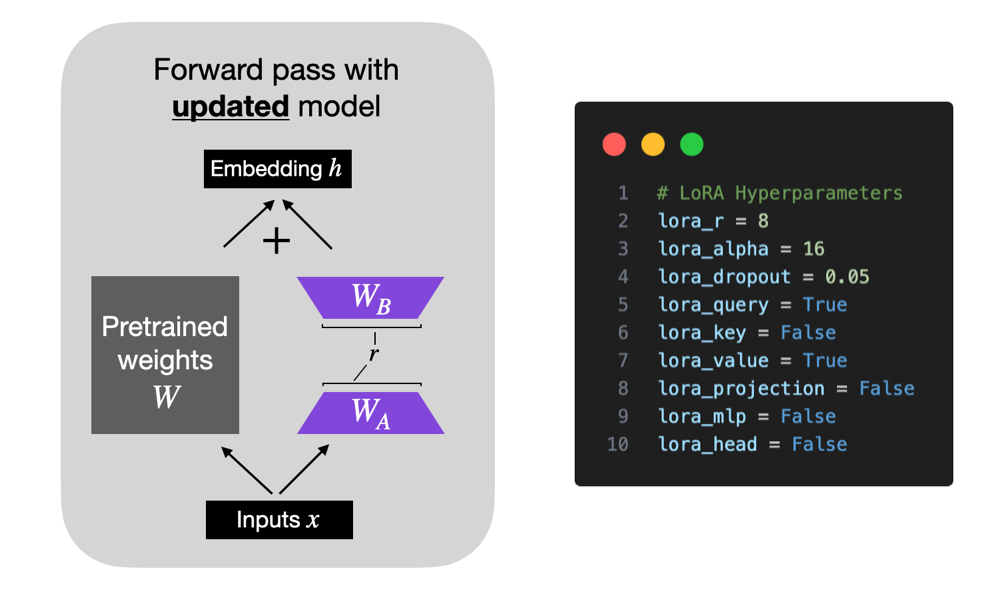
Example of LoRA for Image Classification
pip install transformers accelerate peft datasets evaluatefrom datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("food101", split="train[:5000]")labels = dataset.features["label"].names
label2id, id2label = dict(), dict()
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
label2id[label] = i
id2label[i] = labelWe’ll use this model: https://huggingface.co/google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k
model_checkpoint = "google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k"from torchvision.transforms import (
CenterCrop,
Compose,
Normalize,
RandomHorizontalFlip,
RandomResizedCrop,
Resize,
ToTensor,
)
normalize = Normalize(mean=image_processor.image_mean, std=image_processor.image_std)
train_transforms = Compose(
[
RandomResizedCrop(image_processor.size["height"]),
RandomHorizontalFlip(),
ToTensor(),
normalize,
]
)
val_transforms = Compose(
[
Resize(image_processor.size["height"]),
CenterCrop(image_processor.size["height"]),
ToTensor(),
normalize,
]
)
def preprocess_train(example_batch):
"""Apply train_transforms across a batch."""
example_batch["pixel_values"] = [train_transforms(image.convert("RGB")) for image in example_batch["image"]]
return example_batch
def preprocess_val(example_batch):
"""Apply val_transforms across a batch."""
example_batch["pixel_values"] = [val_transforms(image.convert("RGB")) for image in example_batch["image"]]
return example_batchsplits = dataset.train_test_split(test_size=0.1)
train_ds = splits["train"]
val_ds = splits["test"]
train_ds.set_transform(preprocess_train)
val_ds.set_transform(preprocess_val)def print_trainable_parameters(model):
trainable_params = 0
all_param = 0
for _, param in model.named_parameters():
all_param += param.numel()
if param.requires_grad:
trainable_params += param.numel()
print(
f"trainable params: {trainable_params} || all params: {all_param} || trainable%: {100 * trainable_params / all_param:.2f}"
)from transformers import AutoModelForImageClassification, TrainingArguments, Trainer
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
model_checkpoint,
label2id=label2id,
id2label=id2label,
ignore_mismatched_sizes=True, # provide this in case you're planning to fine-tune an already fine-tuned checkpoint
)print_trainable_parameters(model)trainable params: 85876325 || all params: 85876325 || trainable%: 100.00from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
config = LoraConfig(
r=16,
lora_alpha=16,
target_modules=["query", "value"],
lora_dropout=0.1,
bias="none",
modules_to_save=["classifier"],
)
lora_model = get_peft_model(model, config)
print_trainable_parameters(lora_model)from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
model_name = model_checkpoint.split("/")[-1]
batch_size = 128
args = TrainingArguments(
f"{model_name}-finetuned-lora-food101",
remove_unused_columns=False,
evaluation_strategy="epoch",
save_strategy="epoch",
learning_rate=5e-3,
per_device_train_batch_size=batch_size,
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
per_device_eval_batch_size=batch_size,
fp16=True,
num_train_epochs=5,
logging_steps=10,
load_best_model_at_end=True,
metric_for_best_model="accuracy",
label_names=["labels"],
)import numpy as np
import evaluate
metric = evaluate.load("accuracy")
def compute_metrics(eval_pred):
"""Computes accuracy on a batch of predictions"""
predictions = np.argmax(eval_pred.predictions, axis=1)
return metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=eval_pred.label_ids)import torch
def collate_fn(examples):
pixel_values = torch.stack([example["pixel_values"] for example in examples])
labels = torch.tensor([example["label"] for example in examples])
return {"pixel_values": pixel_values, "labels": labels}trainer = Trainer(
lora_model,
args,
train_dataset=train_ds,
eval_dataset=val_ds,
tokenizer=image_processor,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
data_collator=collate_fn,
)
train_results = trainer.train()trainer.evaluate(val_ds)from peft import PeftConfig, PeftModel
config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained("vit-base-patch16-224-in21k-finetuned-lora-food101/checkpoint-45")
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
config.base_model_name_or_path,
label2id=label2id,
id2label=id2label,
ignore_mismatched_sizes=True, # provide this in case you're planning to fine-tune an already fine-tuned checkpoint
)
# Load the LoRA model
inference_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, "vit-base-patch16-224-in21k-finetuned-lora-food101/checkpoint-45")Inference
from PIL import Image
import requests
url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/sayakpaul/sample-datasets/resolve/main/beignets.jpeg"
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
image
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("vit-base-patch16-224-in21k-finetuned-lora-food101/checkpoint-45")encoding = image_processor(image.convert("RGB"), return_tensors="pt")with torch.no_grad():
outputs = inference_model(**encoding)
logits = outputs.logits
predicted_class_idx = logits.argmax(-1).item()
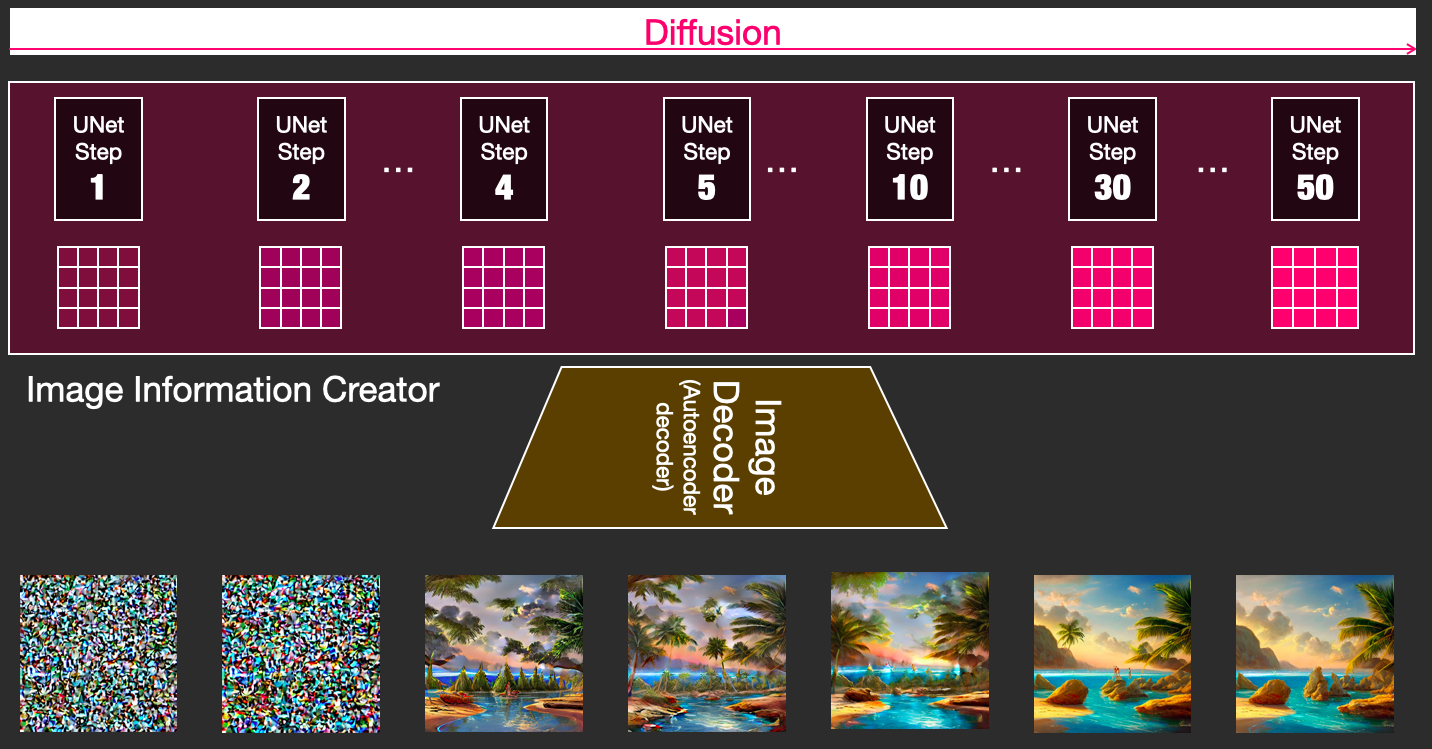
print("Predicted class:", inference_model.config.id2label[predicted_class_idx])Stable Diffusion
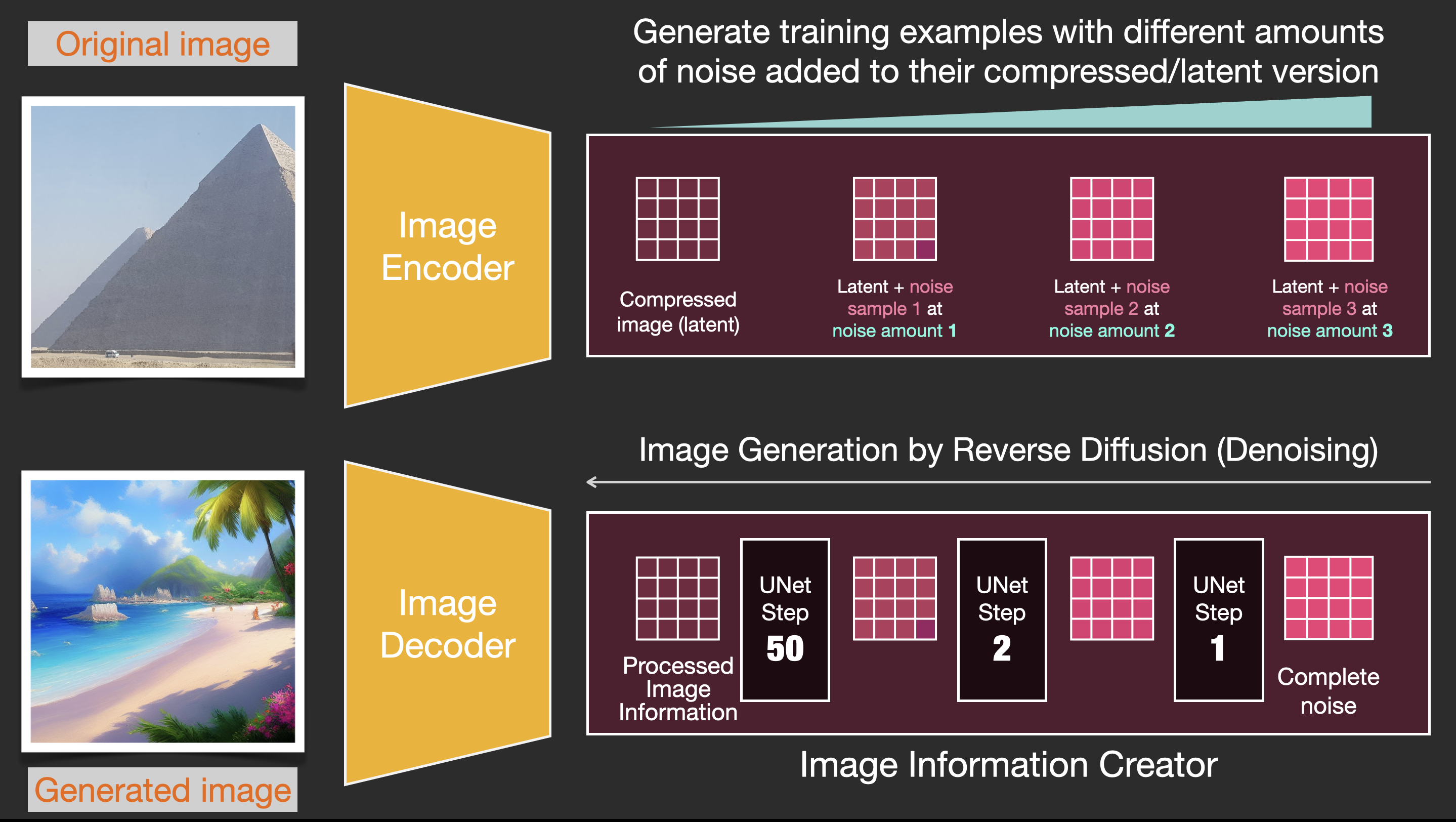
https://jalammar.github.io/illustrated-stable-diffusion/
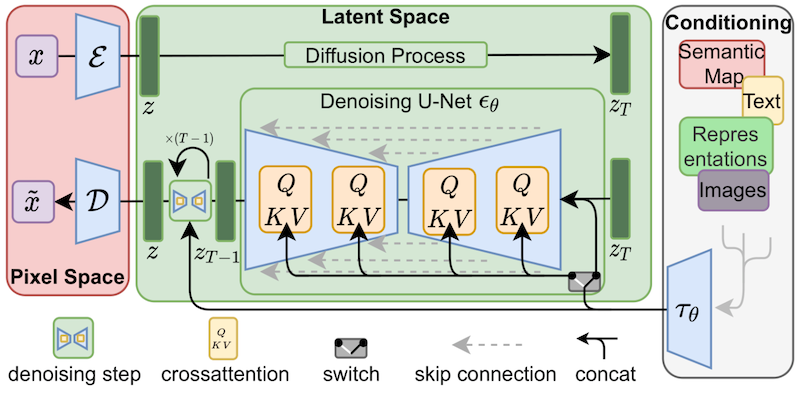
SDXL Architecture
Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.01952
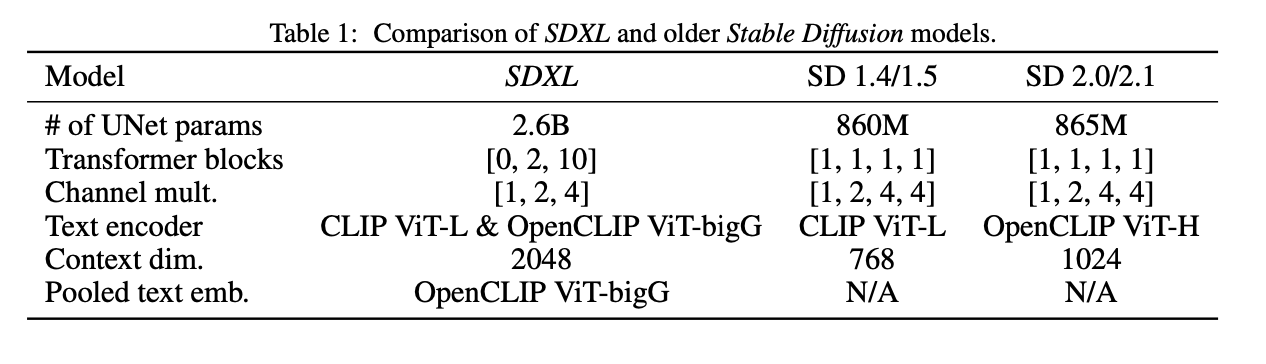
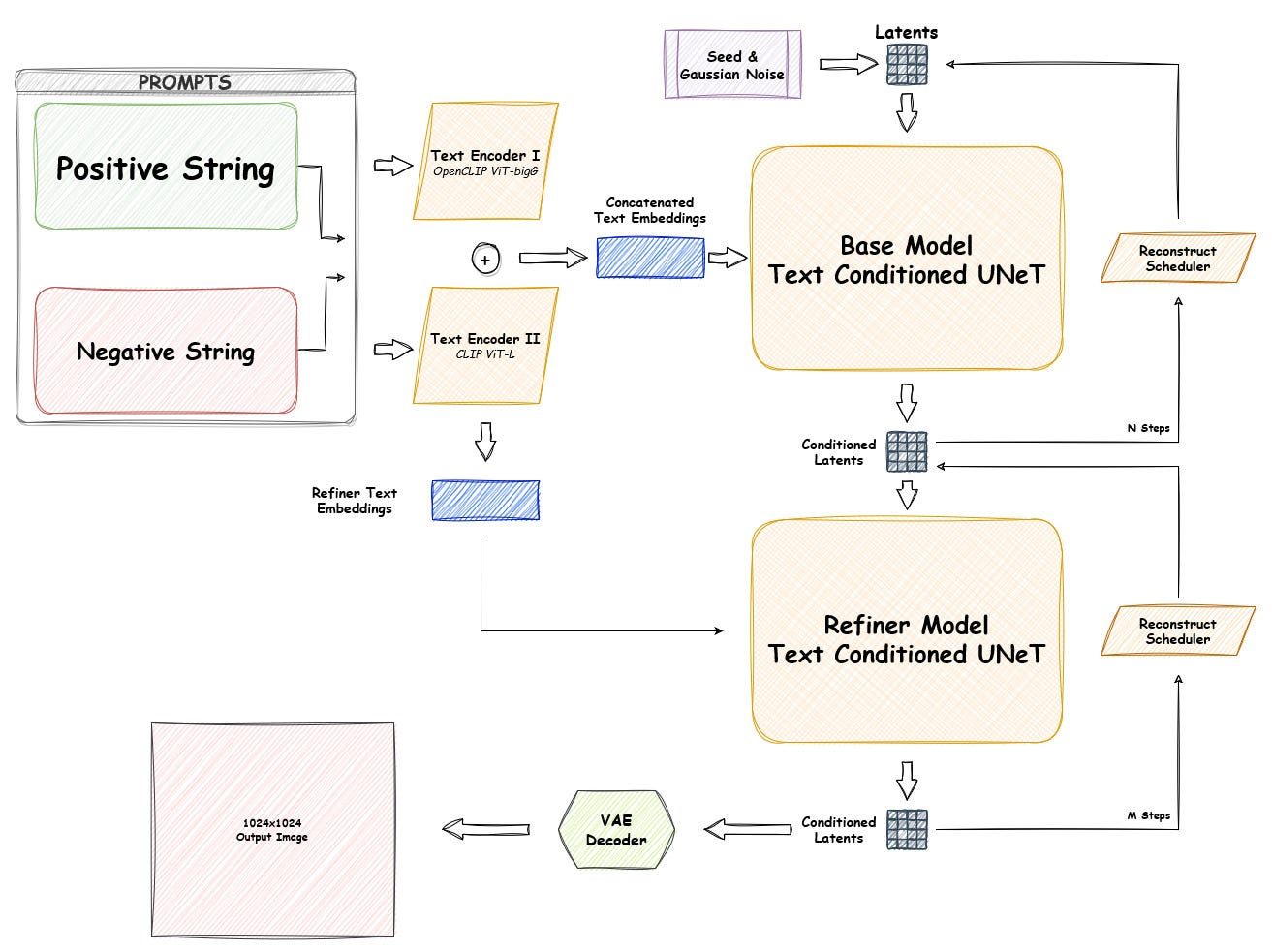
Notice that SDXL has two Text Encoders!
From the paper:
Specifically, we use OpenCLIP ViT-bigG [19] in combination with CLIP ViT-L [34], where we concatenate the penultimate text encoder outputs along the channel-axis [1]. Besides using cross-attention layers to condition the model on the text-input, we follow [30] and additionally condition the model on the pooled text embedding from the OpenCLIP model. These changes result in a model size of 2.6B parameters in the UNet
one model (OpenCLIP-ViT/G) is trained on subjectivity of the image the other (CLIP-ViT/L) is stronger for attributes of the image.
Here’s a repo comparing playing around with prompts
https://github.com/Markus-Pobitzer/sdxl_prompt_test/tree/main
https://mybyways.com/blog/two-text-prompts-text-encoders-in-sdxl-1-0
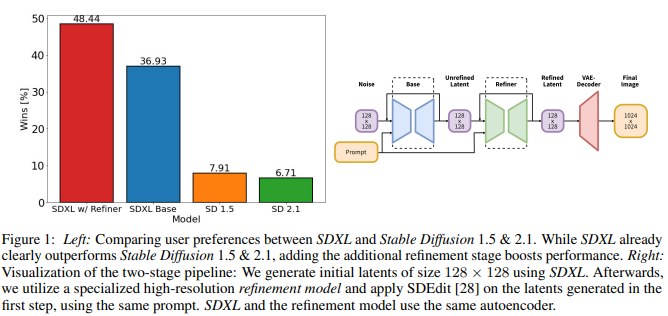


The SDXL Latent Space: https://huggingface.co/blog/TimothyAlexisVass/explaining-the-sdxl-latent-space
DreamBooth
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.12242
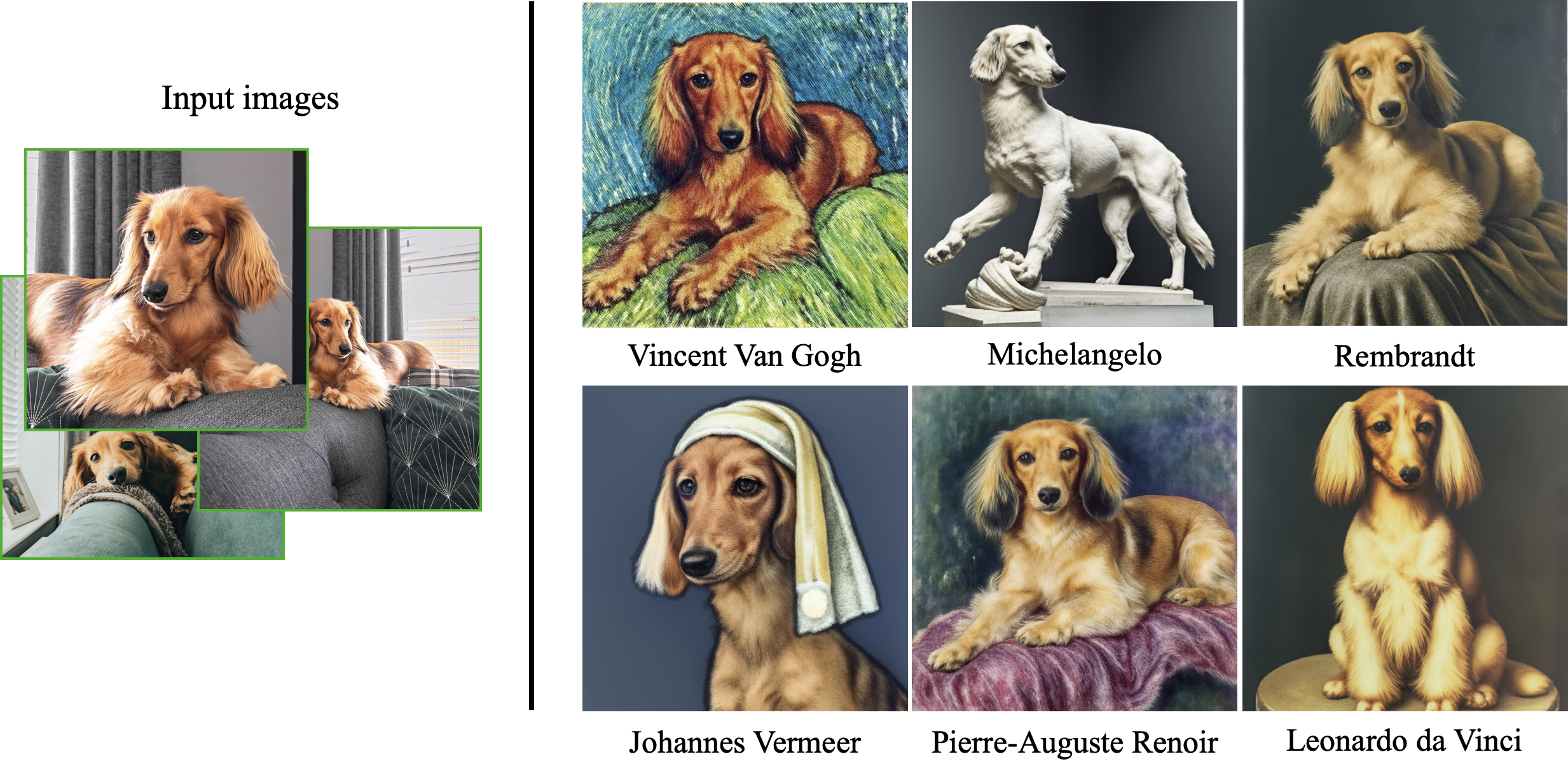
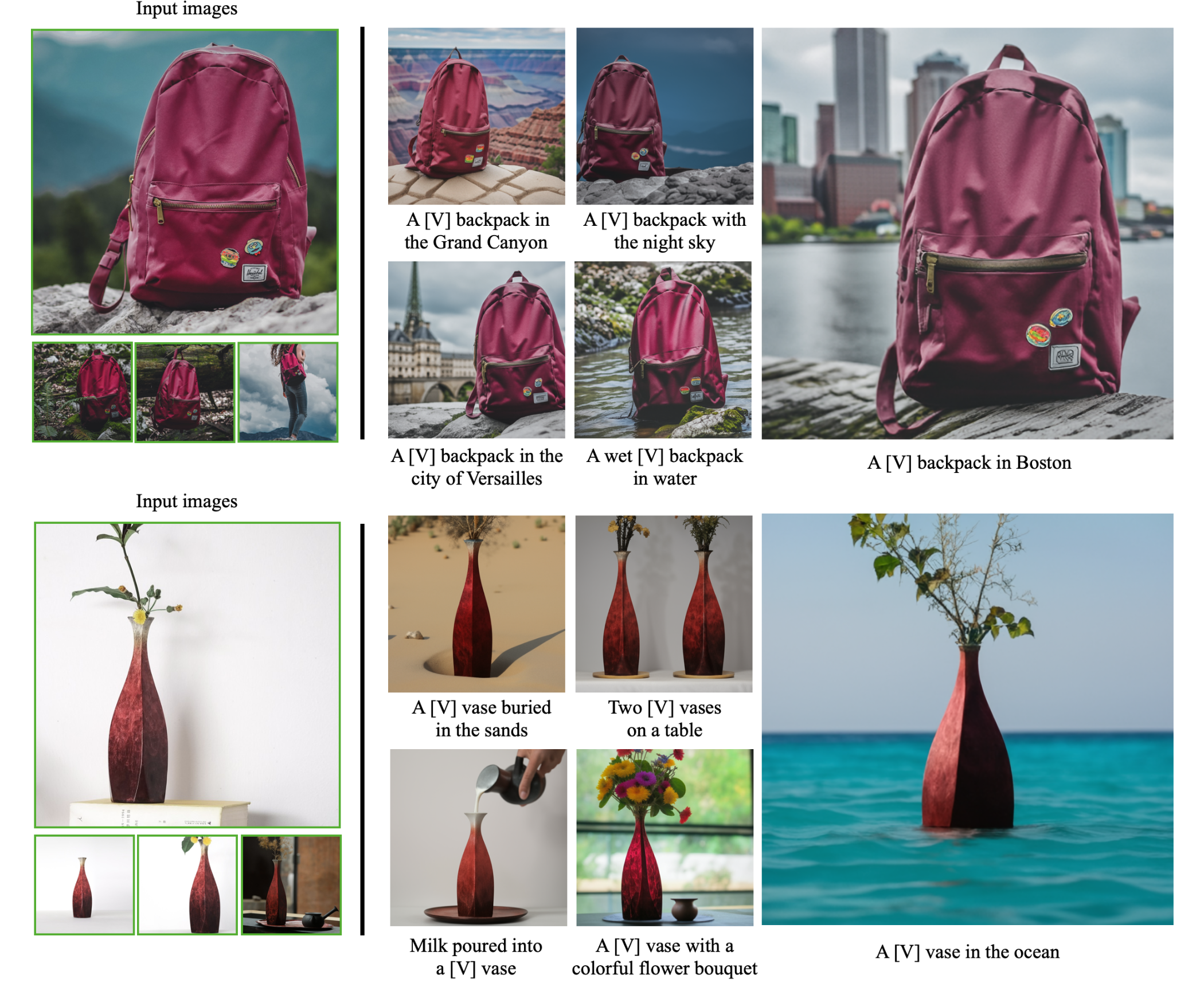
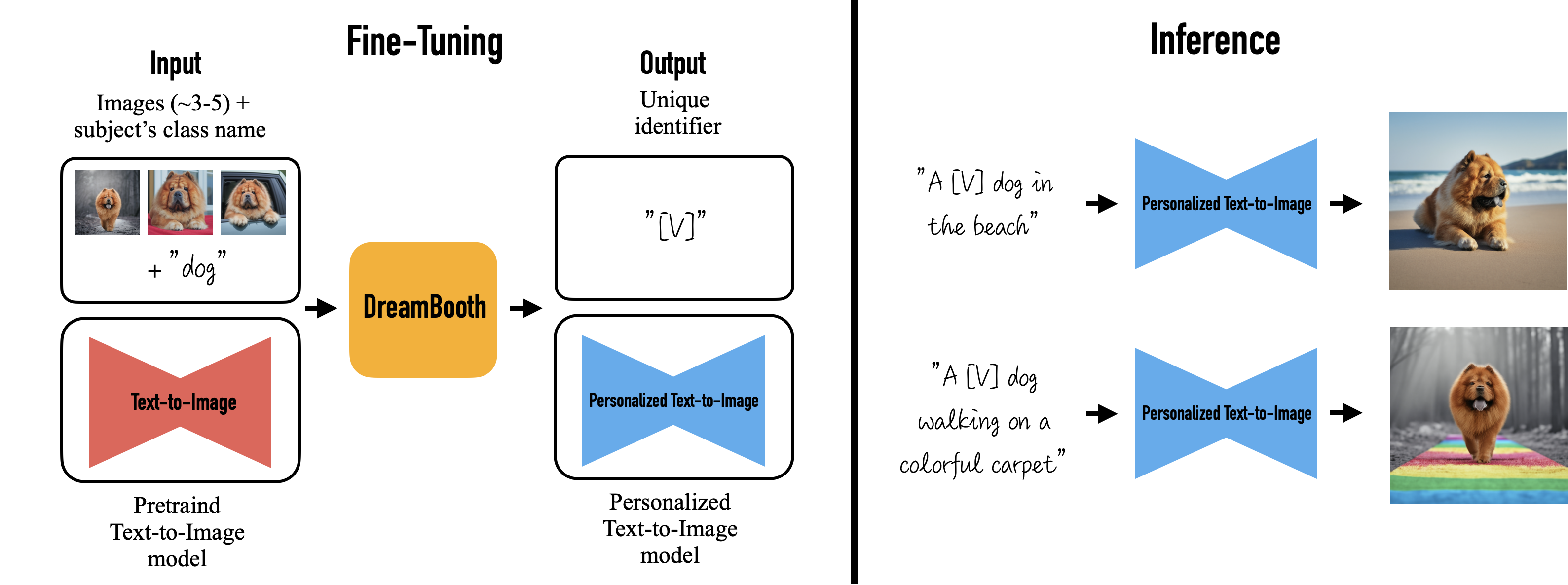



Create a Jupyter Lab Instance where we will run DreamBooth
pip uninstall peftpip install xformers bitsandbytes transformers acceleratepip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.gitpip install tensorboard tensorboardXaccelerate config~/.cache/huggingface/accelerate/default_config.yaml
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
debug: false
distributed_type: 'NO'
downcast_bf16: 'no'
gpu_ids: all
machine_rank: 0
main_training_function: main
mixed_precision: fp16
num_machines: 1
num_processes: 1
rdzv_backend: static
same_network: true
tpu_env: []
tpu_use_cluster: false
tpu_use_sudo: false
use_cpu: falseTraining on the sample dog dataset
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
local_dir = "./dog"
snapshot_download(
"diffusers/dog-example",
local_dir=local_dir, repo_type="dataset",
ignore_patterns=".gitattributes",
)from PIL import Image
def image_grid(imgs, rows, cols, resize=256):
assert len(imgs) == rows * cols
if resize is not None:
imgs = [img.resize((resize, resize)) for img in imgs]
w, h = imgs[0].size
grid = Image.new("RGB", size=(cols * w, rows * h))
grid_w, grid_h = grid.size
for i, img in enumerate(imgs):
grid.paste(img, box=(i % cols * w, i // cols * h))
return gridimport glob
imgs = [Image.open(path) for path in glob.glob("./dog/*.jpeg")]
image_grid(imgs, 1, 5)
MODEL_NAME="stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
INSTANCE_DIR="dog"
OUTPUT_DIR="lora-trained-xl"
VAE_PATH="madebyollin/sdxl-vae-fp16-fix"! accelerate launch sdxl.py \
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
--pretrained_vae_model_name_or_path=$VAE_PATH \
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
--mixed_precision="fp16" \
--instance_prompt="a photo of sks dog" \
--resolution=512 \
--train_batch_size=1 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps=4 \
--gradient_checkpointing \
--learning_rate=1e-4 \
--report_to="tensorboard" \
--lr_scheduler="constant" \
--lr_warmup_steps=0 \
--max_train_steps=200 \
--use_8bit_adam \
--checkpointing_steps=717 \
--seed="0"Steps: 100%|███████████| 200/200 [11:15<00:00, 3.38s/it, loss=0.297, lr=0.0001]Inference
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
import torchpipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")pipe.load_lora_weights("./lora-trained-xl")image = pipe("A picture of a sks dog with a cat", num_inference_steps=25).images[0]
You can do this on Colab as well! https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1sPFKQcdnX3nVnB6oQSJaC-I3kYL1ookl
Training on Custom Dataset
We’re going to strip down the original implementation to make it easier to understand
https://github.com/satyajitghana/sdxl-dreambooth-finetune
dreambooth.py
import gc
import logging
import math
import os
from enum import Enum
from pathlib import Path
import diffusers
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import transformers
from accelerate import Accelerator
from accelerate.logging import get_logger
from accelerate.utils import (DistributedDataParallelKwargs,
ProjectConfiguration, set_seed)
from diffusers import (AutoencoderKL, DDPMScheduler,
DPMSolverMultistepScheduler, StableDiffusionXLPipeline,
UNet2DConditionModel)
from diffusers.loaders import LoraLoaderMixin
from diffusers.models.lora import LoRALinearLayer
from diffusers.optimization import get_scheduler
from diffusers.training_utils import compute_snr, unet_lora_state_dict
from diffusers.utils import check_min_version, is_wandb_available
from diffusers.utils.import_utils import is_xformers_available
from rich import print
from rich.logging import RichHandler
from rich.progress import Progress
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from tqdm.rich import tqdm
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, PretrainedConfig
from dataset.dreambooth import DreamBoothDataset, collate_fn
class MixedPrecisionType(str, Enum):
no = "no"
fp16 = "fp16"
bf16 = "bf16"
logger = get_logger(__name__)
def import_model_class_from_model_name_or_path(
pretrained_model_name_or_path: str,
revision: str = None,
subfolder: str = "text_encoder",
):
text_encoder_config = PretrainedConfig.from_pretrained(
pretrained_model_name_or_path, subfolder=subfolder, revision=revision
)
model_class = text_encoder_config.architectures[0]
if model_class == "CLIPTextModel":
from transformers import CLIPTextModel
return CLIPTextModel
elif model_class == "CLIPTextModelWithProjection":
from transformers import CLIPTextModelWithProjection
return CLIPTextModelWithProjection
else:
raise ValueError(f"{model_class} is not supported.")
# TODO: This function should be removed once training scripts are rewritten in PEFT
def text_encoder_lora_state_dict(text_encoder):
state_dict = {}
def text_encoder_attn_modules(text_encoder):
from transformers import CLIPTextModel, CLIPTextModelWithProjection
attn_modules = []
if isinstance(text_encoder, (CLIPTextModel, CLIPTextModelWithProjection)):
for i, layer in enumerate(text_encoder.text_model.encoder.layers):
name = f"text_model.encoder.layers.{i}.self_attn"
mod = layer.self_attn
attn_modules.append((name, mod))
return attn_modules
for name, module in text_encoder_attn_modules(text_encoder):
for k, v in module.q_proj.lora_linear_layer.state_dict().items():
state_dict[f"{name}.q_proj.lora_linear_layer.{k}"] = v
for k, v in module.k_proj.lora_linear_layer.state_dict().items():
state_dict[f"{name}.k_proj.lora_linear_layer.{k}"] = v
for k, v in module.v_proj.lora_linear_layer.state_dict().items():
state_dict[f"{name}.v_proj.lora_linear_layer.{k}"] = v
for k, v in module.out_proj.lora_linear_layer.state_dict().items():
state_dict[f"{name}.out_proj.lora_linear_layer.{k}"] = v
return state_dict
def tokenize_prompt(tokenizer, prompt):
text_inputs = tokenizer(
prompt,
padding="max_length",
max_length=tokenizer.model_max_length,
truncation=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
text_input_ids = text_inputs.input_ids
return text_input_ids
# Adapted from pipelines.StableDiffusionXLPipeline.encode_prompt
def encode_prompt(text_encoders, tokenizers, prompt, text_input_ids_list=None):
prompt_embeds_list = []
for i, text_encoder in enumerate(text_encoders):
if tokenizers is not None:
tokenizer = tokenizers[i]
text_input_ids = tokenize_prompt(tokenizer, prompt)
else:
assert text_input_ids_list is not None
text_input_ids = text_input_ids_list[i]
prompt_embeds = text_encoder(
text_input_ids.to(text_encoder.device), output_hidden_states=True,
)
# We are only ALWAYS interested in the pooled output of the final text encoder
pooled_prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds[0]
prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds.hidden_states[-2]
bs_embed, seq_len, _ = prompt_embeds.shape
prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds.view(bs_embed, seq_len, -1)
prompt_embeds_list.append(prompt_embeds)
prompt_embeds = torch.concat(prompt_embeds_list, dim=-1)
pooled_prompt_embeds = pooled_prompt_embeds.view(bs_embed, -1)
return prompt_embeds, pooled_prompt_embeds
def train(
input_images_dir: str,
instance_prompt: str,
base_model: str,
pretrained_vae: str,
resolution: int,
train_batch_size: int,
max_train_steps: int,
gradient_accumulation_steps: int,
learning_rate: float,
use_8bit_adam: bool,
use_tf32: bool,
mixed_precision: MixedPrecisionType,
lora_rank: int,
output_dir: str,
):
logging_dir = Path(output_dir, output_dir)
accelerator_project_config = ProjectConfiguration(
project_dir=output_dir, logging_dir=logging_dir
)
kwargs = DistributedDataParallelKwargs(find_unused_parameters=True)
accelerator = Accelerator(
gradient_accumulation_steps=gradient_accumulation_steps,
mixed_precision=mixed_precision.value,
log_with="tensorboard",
project_config=accelerator_project_config,
kwargs_handlers=[kwargs],
)
logging.basicConfig(
format="%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(name)s - %(message)s",
datefmt="%d/%m/%Y %H:%M:%S",
level=logging.INFO,
handlers=[RichHandler(markup=True)],
)
logger.info(accelerator.state, main_process_only=False)
if accelerator.is_local_main_process:
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_warning()
diffusers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_info()
else:
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_error()
diffusers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_error()
if accelerator.is_main_process:
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# Load the tokenizers
logger.info("loading tokenizers")
tokenizer_one = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
base_model, subfolder="tokenizer", use_fast=False,
)
tokenizer_two = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
base_model, subfolder="tokenizer_2", use_fast=False,
)
# import correct text encoder classes
text_encoder_cls_one = import_model_class_from_model_name_or_path(base_model)
text_encoder_cls_two = import_model_class_from_model_name_or_path(
base_model, subfolder="text_encoder_2"
)
# Load scheduler and models
noise_scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained(base_model, subfolder="scheduler")
text_encoder_one = text_encoder_cls_one.from_pretrained(
base_model, subfolder="text_encoder",
)
text_encoder_two = text_encoder_cls_two.from_pretrained(
base_model, subfolder="text_encoder_2",
)
vae_path = base_model if pretrained_vae is None else pretrained_vae
logger.info("loading vae")
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained(
vae_path, subfolder="vae" if pretrained_vae is None else None,
)
logger.info("lading unet")
unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(base_model, subfolder="unet")
logger.info(f"unet params = {unet.num_parameters()}")
# We only train the additional adapter LoRA layers
vae.requires_grad_(False)
text_encoder_one.requires_grad_(False)
text_encoder_two.requires_grad_(False)
unet.requires_grad_(False)
# For mixed precision training we cast all non-trainable weights (vae, non-lora text_encoder and non-lora unet) to half-precision
# as these weights are only used for inference, keeping weights in full precision is not required.
weight_dtype = torch.float32
if accelerator.mixed_precision == "fp16":
weight_dtype = torch.float16
elif accelerator.mixed_precision == "bf16":
weight_dtype = torch.bfloat16
# Move unet, vae and text_encoder to device and cast to weight_dtype
unet.to(accelerator.device, dtype=weight_dtype)
# The VAE is always in float32 to avoid NaN losses.
vae.to(accelerator.device, dtype=torch.float32)
text_encoder_one.to(accelerator.device, dtype=weight_dtype)
text_encoder_two.to(accelerator.device, dtype=weight_dtype)
# now we will add new LoRA weights to the attention layers
# Set correct lora layers
unet_lora_parameters = []
for attn_processor_name, attn_processor in unet.attn_processors.items():
# Parse the attention module.
attn_module = unet
for n in attn_processor_name.split(".")[:-1]:
attn_module = getattr(attn_module, n)
# Set the `lora_layer` attribute of the attention-related matrices.
attn_module.to_q.set_lora_layer(
LoRALinearLayer(
in_features=attn_module.to_q.in_features,
out_features=attn_module.to_q.out_features,
rank=lora_rank,
)
)
attn_module.to_k.set_lora_layer(
LoRALinearLayer(
in_features=attn_module.to_k.in_features,
out_features=attn_module.to_k.out_features,
rank=lora_rank,
)
)
attn_module.to_v.set_lora_layer(
LoRALinearLayer(
in_features=attn_module.to_v.in_features,
out_features=attn_module.to_v.out_features,
rank=lora_rank,
)
)
attn_module.to_out[0].set_lora_layer(
LoRALinearLayer(
in_features=attn_module.to_out[0].in_features,
out_features=attn_module.to_out[0].out_features,
rank=lora_rank,
)
)
# Accumulate the LoRA params to optimize.
unet_lora_parameters.extend(attn_module.to_q.lora_layer.parameters())
unet_lora_parameters.extend(attn_module.to_k.lora_layer.parameters())
unet_lora_parameters.extend(attn_module.to_v.lora_layer.parameters())
unet_lora_parameters.extend(attn_module.to_out[0].lora_layer.parameters())
logger.info(
f"training lora parameters = {sum(p.numel() for p in unet_lora_parameters)}"
)
# create custom saving & loading hooks so that `accelerator.save_state(...)` serializes in a nice format
def save_model_hook(models, weights, output_dir):
if accelerator.is_main_process:
# there are only two options here. Either are just the unet attn processor layers
# or there are the unet and text encoder atten layers
unet_lora_layers_to_save = None
text_encoder_one_lora_layers_to_save = None
text_encoder_two_lora_layers_to_save = None
for model in models:
if isinstance(model, type(accelerator.unwrap_model(unet))):
unet_lora_layers_to_save = unet_lora_state_dict(model)
elif isinstance(
model, type(accelerator.unwrap_model(text_encoder_one))
):
text_encoder_one_lora_layers_to_save = text_encoder_lora_state_dict(
model
)
elif isinstance(
model, type(accelerator.unwrap_model(text_encoder_two))
):
text_encoder_two_lora_layers_to_save = text_encoder_lora_state_dict(
model
)
else:
raise ValueError(f"unexpected save model: {model.__class__}")
# make sure to pop weight so that corresponding model is not saved again
weights.pop()
StableDiffusionXLPipeline.save_lora_weights(
output_dir,
unet_lora_layers=unet_lora_layers_to_save,
text_encoder_lora_layers=text_encoder_one_lora_layers_to_save,
text_encoder_2_lora_layers=text_encoder_two_lora_layers_to_save,
)
def load_model_hook(models, input_dir):
unet_ = None
text_encoder_one_ = None
text_encoder_two_ = None
while len(models) > 0:
model = models.pop()
if isinstance(model, type(accelerator.unwrap_model(unet))):
unet_ = model
elif isinstance(model, type(accelerator.unwrap_model(text_encoder_one))):
text_encoder_one_ = model
elif isinstance(model, type(accelerator.unwrap_model(text_encoder_two))):
text_encoder_two_ = model
else:
raise ValueError(f"unexpected save model: {model.__class__}")
lora_state_dict, network_alphas = LoraLoaderMixin.lora_state_dict(input_dir)
LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_into_unet(
lora_state_dict, network_alphas=network_alphas, unet=unet_
)
text_encoder_state_dict = {
k: v for k, v in lora_state_dict.items() if "text_encoder." in k
}
LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_into_text_encoder(
text_encoder_state_dict,
network_alphas=network_alphas,
text_encoder=text_encoder_one_,
)
text_encoder_2_state_dict = {
k: v for k, v in lora_state_dict.items() if "text_encoder_2." in k
}
LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_into_text_encoder(
text_encoder_2_state_dict,
network_alphas=network_alphas,
text_encoder=text_encoder_two_,
)
accelerator.register_save_state_pre_hook(save_model_hook)
accelerator.register_load_state_pre_hook(load_model_hook)
# Enable TF32 for faster training on Ampere GPUs,
# cf https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/cuda.html#tensorfloat-32-tf32-on-ampere-devices
if use_tf32:
logger.info(":fire: using Ampere TF32")
torch.backends.cuda.matmul.allow_tf32 = True
# Optimization parameters
unet_lora_parameters_with_lr = {
"params": unet_lora_parameters,
"lr": learning_rate,
}
params_to_optimize = [unet_lora_parameters_with_lr]
# optimizer
if use_8bit_adam:
try:
import bitsandbytes as bnb
except ImportError:
raise ImportError(
"To use 8-bit Adam, please install the bitsandbytes library: `pip install bitsandbytes`."
)
logger.info("using bnb adam 8 bit")
optimizer_class = bnb.optim.AdamW8bit
else:
logger.info("using torch AdamW")
optimizer_class = torch.optim.AdamW
optimizer = optimizer_class(
params_to_optimize, betas=(0.9, 0.999), weight_decay=1e-4, eps=1e-8,
)
train_dataset = DreamBoothDataset(
images_dir=input_images_dir, prompt=instance_prompt, size=resolution
)
train_dataloader = DataLoader(
train_dataset, batch_size=train_batch_size, shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn
)
# Computes additional embeddings/ids required by the SDXL UNet.
# regular text embeddings (when `train_text_encoder` is not True)
# pooled text embeddings
# time ids
def compute_time_ids():
# Adapted from pipeline.StableDiffusionXLPipeline._get_add_time_ids
original_size = (resolution, resolution)
target_size = (resolution, resolution)
add_time_ids = list(original_size + (0, 0) + target_size)
add_time_ids = torch.tensor([add_time_ids])
add_time_ids = add_time_ids.to(accelerator.device, dtype=weight_dtype)
return add_time_ids
tokenizers = [tokenizer_one, tokenizer_two]
text_encoders = [text_encoder_one, text_encoder_two]
def compute_text_embeddings(prompt, text_encoders, tokenizers):
with torch.no_grad():
prompt_embeds, pooled_prompt_embeds = encode_prompt(
text_encoders, tokenizers, prompt
)
prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds.to(accelerator.device)
pooled_prompt_embeds = pooled_prompt_embeds.to(accelerator.device)
return prompt_embeds, pooled_prompt_embeds
# Handle instance prompt.
logger.info(":construction: computing time ids")
instance_time_ids = compute_time_ids()
# precompute prompt embeddings to save time
logger.info("precomputing text embeddings")
(
instance_prompt_hidden_states,
instance_pooled_prompt_embeds,
) = compute_text_embeddings(instance_prompt, text_encoders, tokenizers)
# save some memory
del tokenizers, text_encoders
gc.collect()
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
add_time_ids = instance_time_ids
prompt_embeds = instance_prompt_hidden_states
unet_add_text_embeds = instance_pooled_prompt_embeds
# prepare the networks
unet, optimizer, train_dataloader = accelerator.prepare(
unet, optimizer, train_dataloader
)
# We need to initialize the trackers we use, and also store our configuration.
# The trackers initializes automatically on the main process.
if accelerator.is_main_process:
accelerator.init_trackers("dreambooth-lora-sd-xl")
total_batch_size = (
train_batch_size * accelerator.num_processes * gradient_accumulation_steps
)
logger.info(
"[bold blue]:running: :running: :running: Training Config :running: :running: :running:"
)
logger.info(f" Num examples = {len(train_dataset)}")
logger.info(f" Num batches each epoch = {len(train_dataloader)}")
logger.info(f" Instantaneous batch size per device = {train_batch_size}")
logger.info(
f" Total train batch size (w. parallel, distributed & accumulation) = {total_batch_size}"
)
logger.info(f" Gradient Accumulation steps = {gradient_accumulation_steps}")
logger.info(f" Total optimization steps = {max_train_steps}")
# We need to recalculate our total training steps as the size of the training dataloader may have changed.
num_update_steps_per_epoch = math.ceil(
len(train_dataloader) / gradient_accumulation_steps
)
num_train_epochs = math.ceil(max_train_steps / num_update_steps_per_epoch)
global_step = 0
first_epoch = 0
initial_global_step = 0
progress_bar = tqdm(
range(0, max_train_steps),
initial=initial_global_step,
desc="Steps",
# Only show the progress bar once on each machine.
disable=not accelerator.is_local_main_process,
)
# epoch
logger.info(":test_tube: start training...")
for epoch in range(num_train_epochs):
unet.train()
# step
for step, batch in enumerate(train_dataloader):
with accelerator.accumulate(unet):
pixel_values = batch["pixel_values"].to(dtype=vae.dtype)
prompts = batch["prompts"]
# Convert images to latent space
model_input = vae.encode(pixel_values).latent_dist.sample()
model_input = model_input * vae.config.scaling_factor
if pretrained_vae is None:
model_input = model_input.to(weight_dtype)
# Sample noise that we'll add to the latents
noise = torch.randn_like(model_input)
bsz = model_input.shape[0]
# Sample a random timestep for each image
timesteps = torch.randint(
0,
noise_scheduler.config.num_train_timesteps,
(bsz,),
device=model_input.device,
)
timesteps = timesteps.long()
# Add noise to the model input according to the noise magnitude at each timestep
# (this is the forward diffusion process)
noisy_model_input = noise_scheduler.add_noise(
model_input, noise, timesteps
)
unet_added_conditions = {
"time_ids": add_time_ids.repeat(bsz, 1),
"text_embeds": unet_add_text_embeds.repeat(bsz, 1),
}
prompt_embeds_input = prompt_embeds.repeat(bsz, 1, 1)
model_pred = unet(
noisy_model_input,
timesteps,
prompt_embeds_input,
added_cond_kwargs=unet_added_conditions,
).sample
# Get the target for loss depending on the prediction type
if noise_scheduler.config.prediction_type == "epsilon":
target = noise
elif noise_scheduler.config.prediction_type == "v_prediction":
target = noise_scheduler.get_velocity(model_input, noise, timesteps)
else:
raise ValueError(
f"Unknown prediction type {noise_scheduler.config.prediction_type}"
)
# compute loss
loss = F.mse_loss(model_pred.float(), target.float(), reduction="mean")
accelerator.backward(loss)
if accelerator.sync_gradients:
params_to_clip = unet_lora_parameters
accelerator.clip_grad_norm_(params_to_clip, max_norm=1.0)
# step
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Checks if the accelerator has performed an optimization step behind the scenes
if accelerator.sync_gradients:
progress_bar.update(1)
global_step += 1
logs = {"loss": loss.detach().item(), "lr": learning_rate}
progress_bar.set_postfix(**logs)
accelerator.log(logs, step=global_step)
if global_step >= max_train_steps:
break
# Save the lora layers
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
if accelerator.is_main_process:
unet = accelerator.unwrap_model(unet)
unet = unet.to(torch.float32)
unet_lora_layers = unet_lora_state_dict(unet)
StableDiffusionXLPipeline.save_lora_weights(
save_directory=output_dir, unet_lora_layers=unet_lora_layers,
)
logger.info(":white_heavy_check_mark: training done!")
logger.info(f":watermelon: saved lora weights in {output_dir}")
logger.info(f"[bold green]:tada: :tada: :tada: ALL DONE :tada: :tada: :tada:")
accelerator.end_training()Take Square Cropped Photos of Yourself

Would be a good idea to take your images with different background and different clothes
Training
accelerate launch main.py dreambooth --input-images-dir ./data/tresa-truck --instance-prompt "a photo of a ohwx truck" --resolution 512 --train-batch-size 1 --max-train-steps 1000 --mixed-precision fp16 --output-dir ./output/tresa-truck07/12/2023 23:36:01 INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:01 - INFO - training.dreambooth - unet params = 2567463684 logging.py:60
07/12/2023 23:36:06 INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:06 - INFO - training.dreambooth - training lora parameters = 5806080 logging.py:60
INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:06 - INFO - training.dreambooth - using torch AdamW logging.py:60
INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:06 - INFO - training.dreambooth - 🚧 computing time ids logging.py:60
INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:06 - INFO - training.dreambooth - precomputing text embeddings logging.py:60
07/12/2023 23:36:07 INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:07 - INFO - training.dreambooth - 🏃 🏃 🏃 Training Config 🏃 🏃 🏃 logging.py:60
INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:07 - INFO - training.dreambooth - Num examples = 8 logging.py:60
INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:07 - INFO - training.dreambooth - Num batches each epoch = 8 logging.py:60
INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:07 - INFO - training.dreambooth - Instantaneous batch size per device = 1 logging.py:60
INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:07 - INFO - training.dreambooth - Total train batch size (w. parallel, distributed & accumulation) = 1 logging.py:60
INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:07 - INFO - training.dreambooth - Gradient Accumulation steps = 1 logging.py:60
INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:07 - INFO - training.dreambooth - Total optimization steps = 1000
INFO 07/12/2023 23:36:07 - INFO - training.dreambooth - 🧪 start training...
07/12/2023 23:47:19 INFO 07/12/2023 23:47:19 - INFO - training.dreambooth - ✅ training done! logging.py:60
INFO 07/12/2023 23:47:19 - INFO - training.dreambooth - 🍉 saved lora weights in ./output/tresa-truck-2 logging.py:60
INFO 07/12/2023 23:47:19 - INFO - training.dreambooth - 🎉 🎉 🎉 ALL DONE 🎉 🎉 🎉 logging.py:60
Steps 100% ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1,000/1,000 [ 0:11:12 < 0:00:00 , 1 it/s ]Trained weights are just 24MB!
❯ du -sh pytorch_lora_weights.safetensors
23M pytorch_lora_weights.safetensorsInference
Compel for Prompt Weighting
Compel is a single-purpose, lightweight library that converts prompt strings to embedding tensors with some handy weighting and blending features.
Prompt weighting works by increasing or decreasing the scale of the text embedding vector that corresponds to its concept in the prompt because you may not necessarily want the model to focus on all concepts equally.
https://github.com/damian0815/compel
Usage with diffusers: https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/using-diffusers/weighted_prompts
pip install compelThe syntax is ("prompt part 1", "prompt part 2").and(). You can have more than one part, and you can also weight them, eg ("a man eating an apple", "sitting on the roof of a car", "high quality, trending on artstation, 8K UHD").and(1, 0.5, 0.5) which will assign weight 1 to man eating an apple and 0.5 to sitting on the roof of a car and high quality, trending on artstation, 8K UHD.
In the new .and() syntax you would prompt this as follows:
("a moist sloppy pindlesackboy sloppy hamblin' bogomadong", "Clem Fandango is pissed-off", "Wario's Woods in background", "making a noise like ga-woink-a").and()Compel SDXL Demo: https://github.com/damian0815/compel/blob/main/compel-demo-sdxl.ipynb
infer.py
from pathlib import Path
import torch
import os
from compel import Compel, ReturnedEmbeddingsType
from diffusers import AutoencoderKL, DiffusionPipeline
from PIL import Image
def image_grid(imgs, rows, cols, resize=256):
assert len(imgs) == rows * cols
if resize is not None:
imgs = [img.resize((resize, resize)) for img in imgs]
w, h = imgs[0].size
grid = Image.new("RGB", size=(cols * w, rows * h))
grid_w, grid_h = grid.size
for i, img in enumerate(imgs):
grid.paste(img, box=(i % cols * w, i // cols * h))
return grid
def infer_lora(
prompt: str,
lora_weights: str,
base_model: str,
pretrained_vae: str,
output_dir: str,
):
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
output_dir = Path(output_dir)
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained(pretrained_vae)
vae.to("cuda", dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
base_model, vae=vae, torch_dtype=torch.float16
)
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
pipe.load_lora_weights(lora_weights)
compel = Compel(
tokenizer=[pipe.tokenizer, pipe.tokenizer_2],
text_encoder=[pipe.text_encoder, pipe.text_encoder_2],
returned_embeddings_type=ReturnedEmbeddingsType.PENULTIMATE_HIDDEN_STATES_NON_NORMALIZED,
requires_pooled=[False, True],
)
conditioning, pooled = compel([prompt] * 4)
images = pipe(
prompt_embeds=conditioning, pooled_prompt_embeds=pooled, num_inference_steps=25,
).images
g = image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=2)
print(f"outputs saved in {output_dir}")
g.save(output_dir / "out_grid.png")
for idx, image in enumerate(images):
image.save(output_dir / f"out_{idx}.png")python main.py infer --prompt "a photo of a ohwx man in a jungle" --lora-weights ./output/tresa-truck --output-dir output/infer-truckSome Outputs



Some Prompts you can try
prompt = "portrait photo of (ohwx man:1.1) wearing an expensive White suit, white background, fit"prompt = "ohwx man (masterpiece:1.5), (close-up shot:1.8), (extremely intricate:1.2), 8k, highly detailed, A delicate pencil sketch of a ohwx man with flowing hair cascading down his shoulders. The sketch captures the man's serene expression"prompt = "ohwx man as an (avenger:1.5), (extremely intricate:1.2), 8k, highly detailed, superhero, marvel comic. (ohwx man:1.2). colorful background"prompt = "cinematic photo (ohwx man:1.2) riding dinosaur in a jungle with mud, sunny day shiny clear sky . 35mm photograph,film,professional,4k,highly detailed, eyeglasses"prompt = "photo of a ohwx man, wearing an expensive suite, 8k, highly detailed, 50mm lens, bokeh effect, fit, ohwx man, wolf of wall street style"You can search for prompts here
- https://stablediffusionweb.com/prompts
- https://huggingface.co/datasets/Gustavosta/Stable-Diffusion-Prompts
- ChatGPT
Stable Diffusion Refiner
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline
from PIL import Imagepipe = StableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-refiner-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16", use_safetensors=True
)
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")init_image = Image.open("generated.png").convert("RGB")
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
image = pipe(prompt, image=init_image).images
image•
• strength (float, optional, defaults to 0.3) — Conceptually, indicates how much to transform the reference image. Must be between 0 and 1. image will be used as a starting point, adding more noise to it the larger the strength. The number of denoising steps depends on the amount of noise initially added. When strength is 1, added noise will be maximum and the denoising process will run for the full number of iterations specified in num_inference_steps. A value of 1, therefore, essentially ignores image. Note that in the case of denoising_start being declared as an integer, the value of strength will be ignored.
Using base and refiner
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
import torch
base = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16", use_safetensors=True
).to("cuda")
refiner = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-refiner-1.0",
text_encoder_2=base.text_encoder_2,
vae=base.vae,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
use_safetensors=True,
variant="fp16",
).to("cuda")Let’s set denoising_end=0.8 so the base model performs the first 80% of denoising the high-noise timesteps and set denoising_start=0.8 so the refiner model performs the last 20% of denoising the low-noise timesteps. The base model output should be in latent space instead of a PIL image.
prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
image = base(
prompt=prompt,
num_inference_steps=40,
denoising_end=0.8,
output_type="latent",
).images
image = refiner(
prompt=prompt,
num_inference_steps=40,
denoising_start=0.8,
image=image,
).images[0]
imageBase to Refiner Model
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
import torch
base = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16", use_safetensors=True
).to("cuda")
refiner = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-refiner-1.0",
text_encoder_2=base.text_encoder_2,
vae=base.vae,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
use_safetensors=True,
variant="fp16",
).to("cuda")prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
image = base(prompt=prompt, output_type="latent").images[0]Generated Image Latents is passed to Refiner
image = refiner(prompt=prompt, image=image[None, :]).images[0]You can also pass the image directly
Before refinement
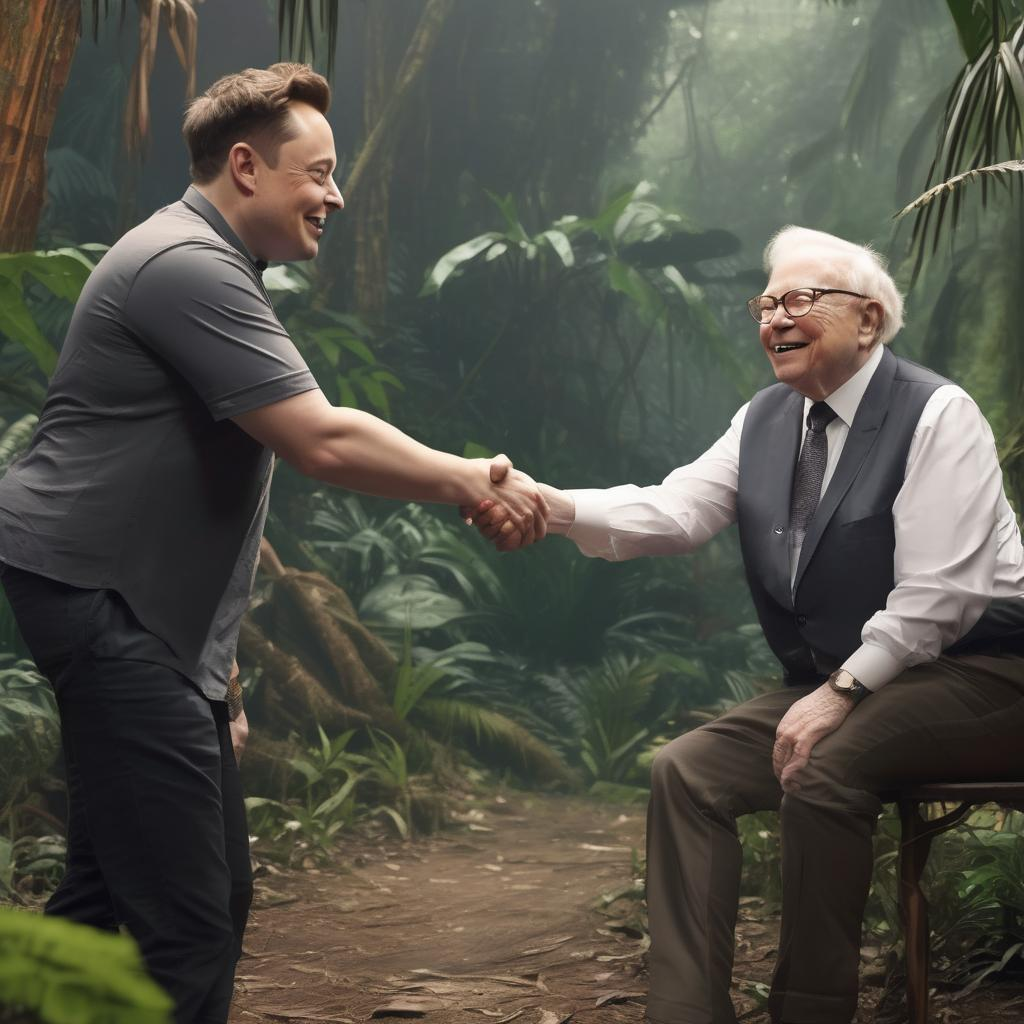
After Refinement
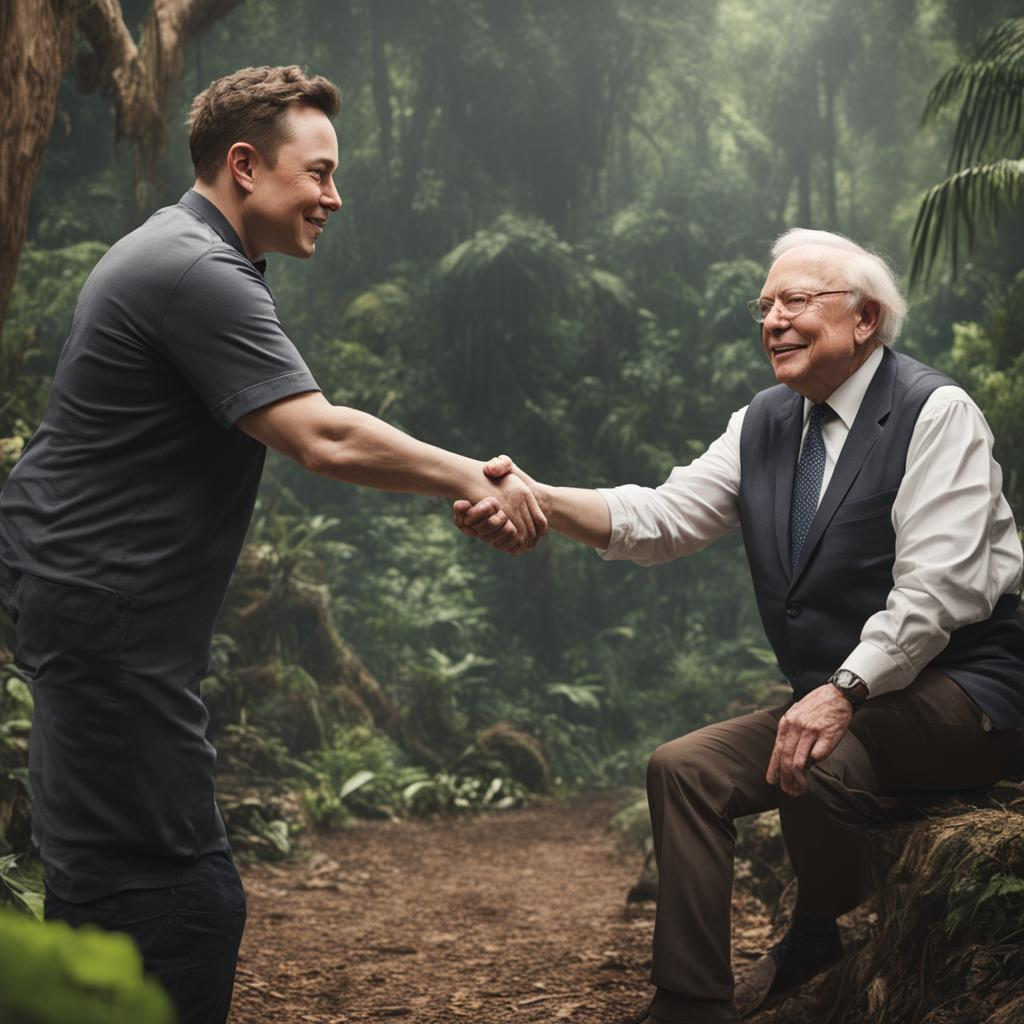

prompt = "realistic closeup photo of Elon Musk shaking hands with Warren Buffett in a jungle, detailed, 8k"
image = base(prompt=prompt).images[0]image_2 = refiner(prompt=prompt, image=image, strength=0.5).images[0]Use a different prompt for each text-encoder
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
import torch
pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16", use_safetensors=True
).to("cuda")
# prompt is passed to OAI CLIP-ViT/L-14
prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
# prompt_2 is passed to OpenCLIP-ViT/bigG-14
prompt_2 = "Van Gogh painting"
image = pipeline(prompt=prompt, prompt_2=prompt_2).images[0]
imageCombining Multiple LoRA’s and Loading/Unloading LoRA
Combining Multiple LoRA
pip install peftfrom diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
from compel import Compel, ReturnedEmbeddingsType
import torch
from PIL import Image
def image_grid(imgs, rows, cols, resize=256):
assert len(imgs) == rows * cols
if resize is not None:
imgs = [img.resize((resize, resize)) for img in imgs]
w, h = imgs[0].size
grid = Image.new("RGB", size=(cols * w, rows * h))
grid_w, grid_h = grid.size
for i, img in enumerate(imgs):
grid.paste(img, box=(i % cols * w, i // cols * h))
return grid
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
pipe.load_lora_weights("./pytorch_lora_weights_satyajit_v1.safetensors", adapter_name="satyajit")
pipe.load_lora_weights("nerijs/pixel-art-xl", weight_name="pixel-art-xl.safetensors", adapter_name="pixel")
pipe.set_adapters(["satyajit", "pixel"], adapter_weights=[0.5, 1.0])
compel = Compel(
tokenizer=[pipe.tokenizer, pipe.tokenizer_2] ,
text_encoder=[pipe.text_encoder, pipe.text_encoder_2],
returned_embeddings_type=ReturnedEmbeddingsType.PENULTIMATE_HIDDEN_STATES_NON_NORMALIZED,
requires_pooled=[False, True]
)
prompt = "portrait of ohwx man, wearing an expensive suit, (pixel art)1.5"
conditioning, pooled = compel([prompt] * 4)
images = pipe(
prompt_embeds=conditioning,
pooled_prompt_embeds=pooled,
num_inference_steps=25,
cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 1.0},
).images
g = image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=2)
g.save("out.png")
for idx, image in enumerate(images):
image.save(f"out_{idx}.png")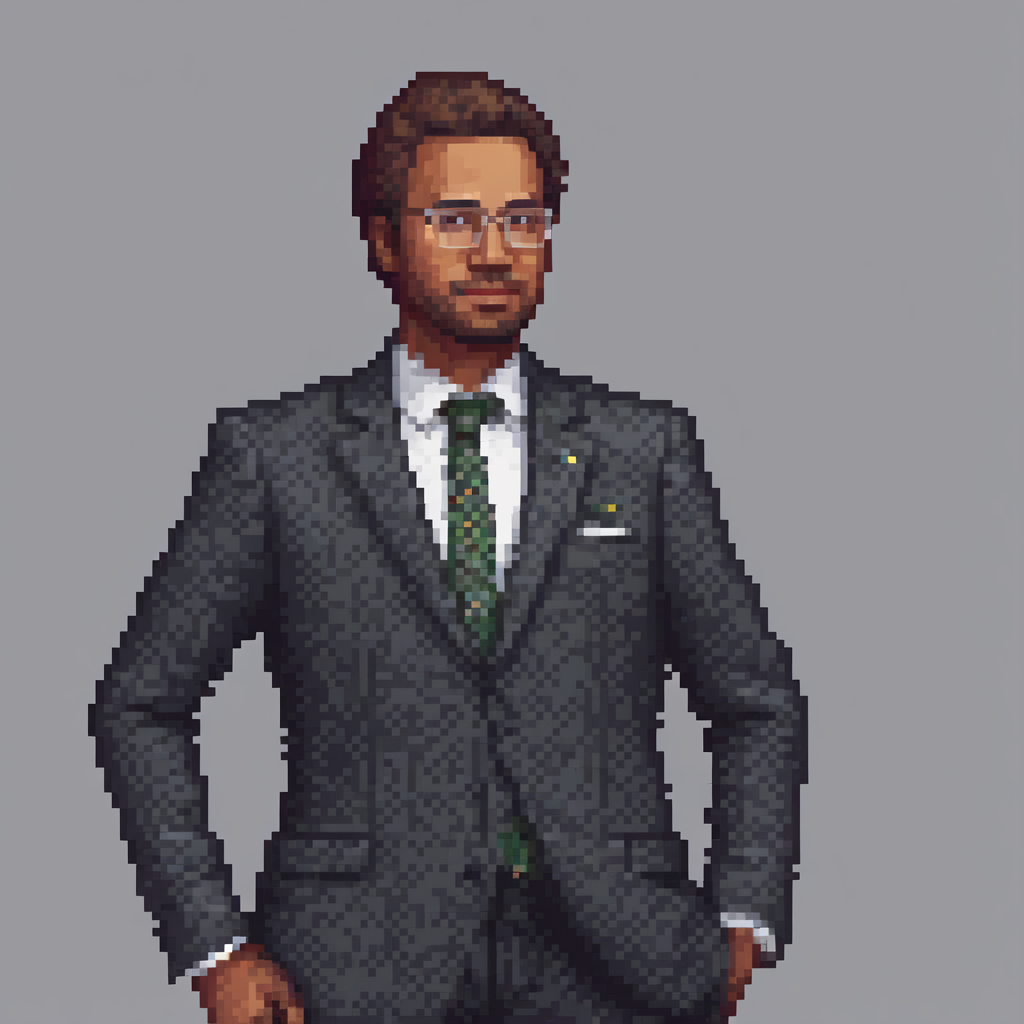
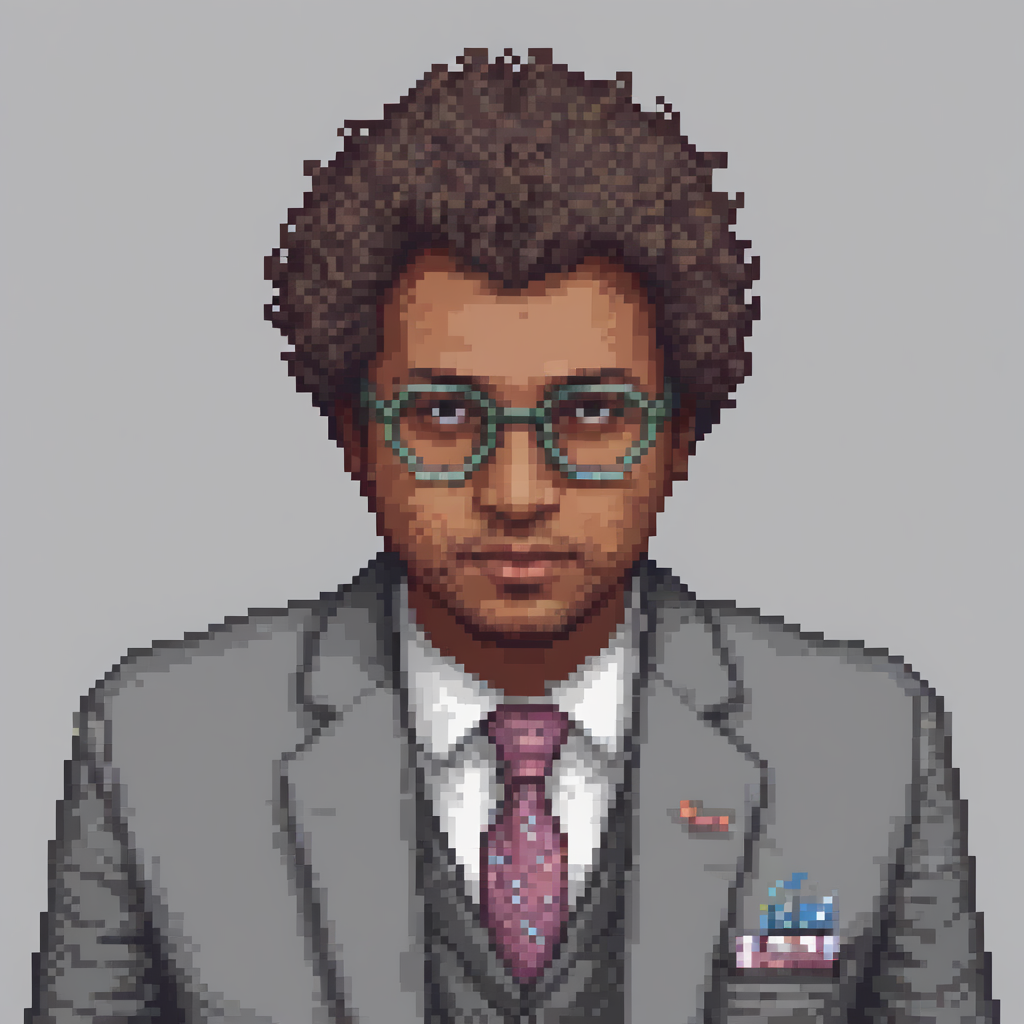
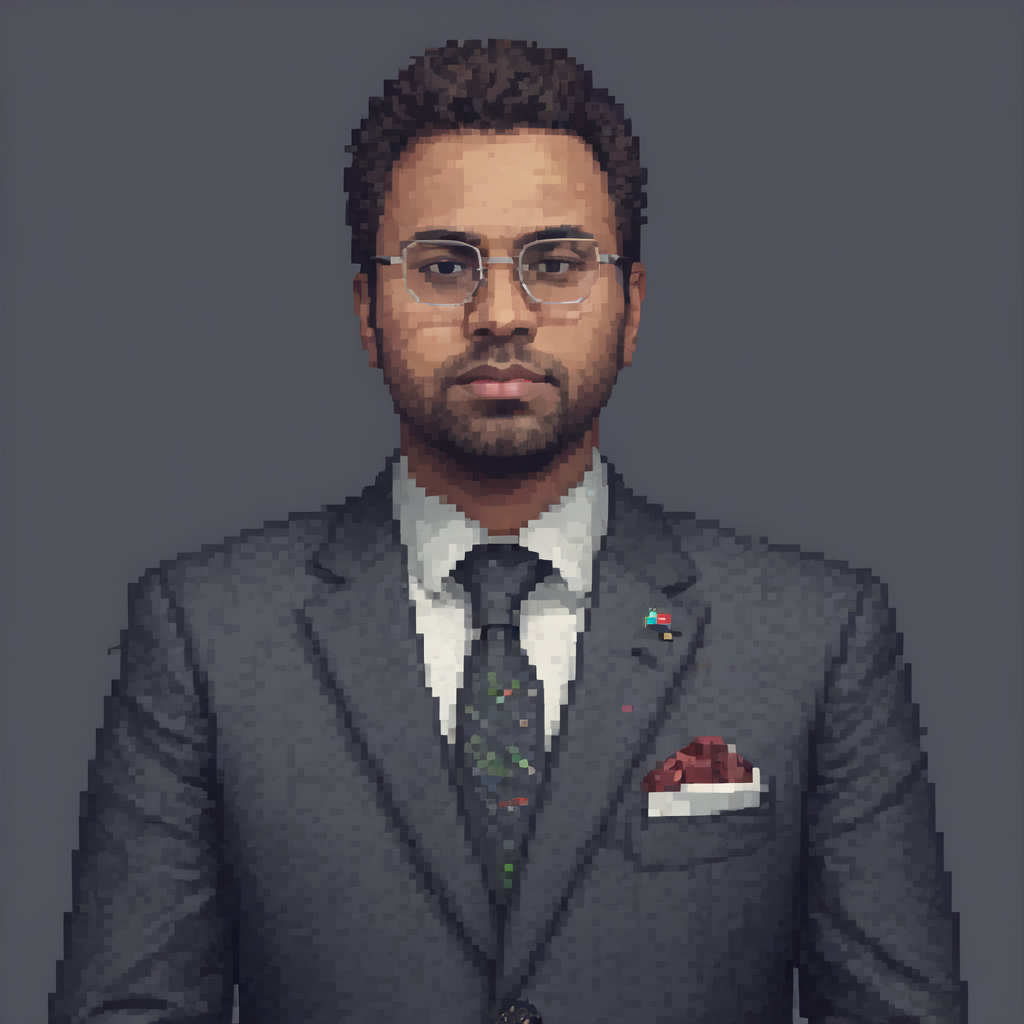


For loading, unloading LoRAs, read this: https://huggingface.co/blog/lora-adapters-dynamic-loading
import torch
from diffusers import (
AutoencoderKL,
DiffusionPipeline,
)
import time
base = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
adapter1 = 'nerijs/pixel-art-xl'
weightname1 = 'pixel-art-xl.safetensors'
adapter2 = 'minimaxir/sdxl-wrong-lora'
weightname2 = None
inputs = "elephant"
kwargs = {}
if torch.cuda.is_available():
kwargs["torch_dtype"] = torch.float16
start = time.time()
# Load VAE compatible with fp16 created by madebyollin
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained(
"madebyollin/sdxl-vae-fp16-fix",
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
)
kwargs["vae"] = vae
kwargs["variant"] = "fp16"
model = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
base, **kwargs
)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model.to("cuda")
elapsed = time.time() - start
print(f"Base model loaded, elapsed {elapsed:.2f} seconds")
def inference(adapter, weightname):
start = time.time()
model.load_lora_weights(adapter, weight_name=weightname)
# Fusing lora weights with the main layers improves inference time by 30 % !
model.fuse_lora()
elapsed = time.time() - start
print(f"LoRA adapter loaded and fused to main model, elapsed {elapsed:.2f} seconds")
start = time.time()
data = model(inputs, num_inference_steps=25).images[0]
elapsed = time.time() - start
print(f"Inference time, elapsed {elapsed:.2f} seconds")
start = time.time()
model.unfuse_lora()
model.unload_lora_weights()
elapsed = time.time() - start
print(f"LoRA adapter unfused/unloaded from base model, elapsed {elapsed:.2f} seconds")
inference(adapter1, weightname1)
inference(adapter2, weightname2)This way you can keep a folder of LoRA weights on S3, and load, unload the weights on-demand!
Stable Video Diffusion
https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/using-diffusers/svd
from diffusers import StableVideoDiffusionPipeline
from diffusers.utils import load_image, export_to_video
import torch
from PIL import Imagepipe = StableVideoDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-video-diffusion-img2vid-xt", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16"
)
pipe.to("cuda")Make sure to crop your image to 1024 x 576
image = Image.open("generated.png")
image = image.convert("RGB")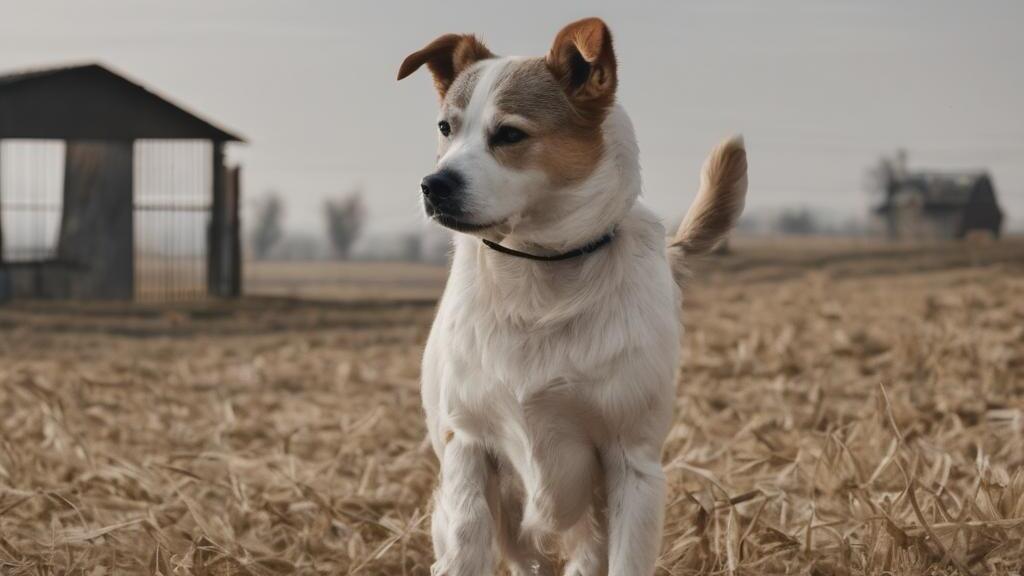
def resize_image(image, output_size=(1024, 576)):
# Calculate aspect ratios
target_aspect = output_size[0] / output_size[1] # Aspect ratio of the desired size
image_aspect = image.width / image.height # Aspect ratio of the original image
# Resize then crop if the original image is larger
if image_aspect > target_aspect:
# Resize the image to match the target height, maintaining aspect ratio
new_height = output_size[1]
new_width = int(new_height * image_aspect)
resized_image = image.resize((new_width, new_height), Image.LANCZOS)
# Calculate coordinates for cropping
left = (new_width - output_size[0]) / 2
top = 0
right = (new_width + output_size[0]) / 2
bottom = output_size[1]
else:
# Resize the image to match the target width, maintaining aspect ratio
new_width = output_size[0]
new_height = int(new_width / image_aspect)
resized_image = image.resize((new_width, new_height), Image.LANCZOS)
# Calculate coordinates for cropping
left = 0
top = (new_height - output_size[1]) / 2
right = output_size[0]
bottom = (new_height + output_size[1]) / 2
# Crop the image
cropped_image = resized_image.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
return cropped_imageAlong with conditioning image Stable Diffusion Video also allows providing micro-conditioning that allows more control over the generated video. It accepts the following arguments:
fps: The frames per second of the generated video.motion_bucket_id: The motion bucket id to use for the generated video. This can be used to control the motion of the generated video. Increasing the motion bucket id will increase the motion of the generated video.noise_aug_strength: The amount of noise added to the conditioning image. The higher the values the less the video will resemble the conditioning image. Increasing this value will also increase the motion of the generated video.
frames = pipe(image, decode_chunk_size=8, motion_bucket_id=180, noise_aug_strength=0.1).frames[0]
export_to_video(frames, "generated.mp4", fps=7)
DeepCache - Accelerating Diffusion Models
https://github.com/horseee/DeepCache
We introduce DeepCache, a novel training-free and almost lossless paradigm that accelerates diffusion models from the perspective of model architecture. Utilizing the property of the U-Net, we reuse the high-level features while updating the low-level features in a very cheap way. DeepCache accelerates Stable Diffusion v1.5 by 2.3x with only a 0.05 decline in CLIP Score, and LDM-4-G(ImageNet) by 4.1x with a 0.22 decrease in FID.
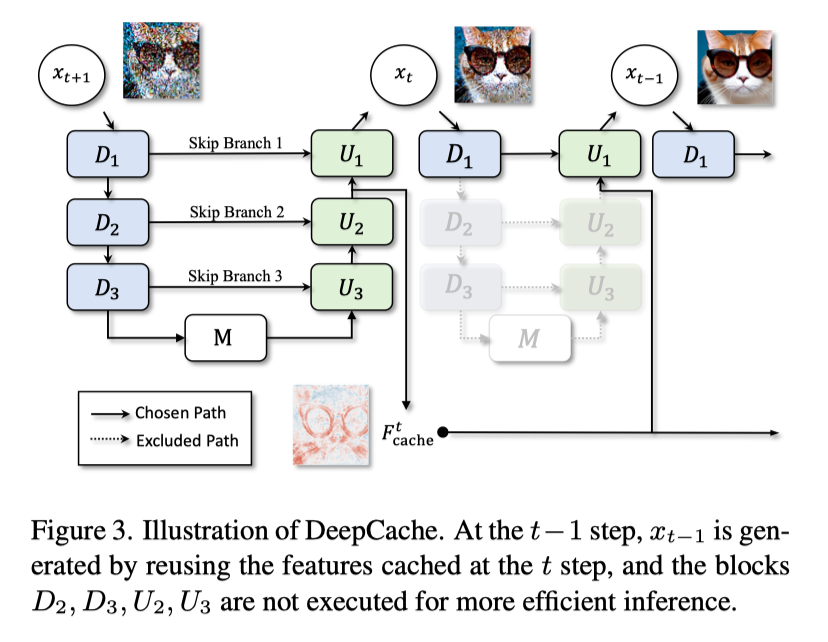
import os
import time
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
import torch
from torchvision.utils import save_image
import argparse
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline, StableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline
from DeepCache import StableDiffusionXLPipeline as DeepCacheStableDiffusionXLPipeline
from DeepCache import StableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline as DeepCacheStableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline
def set_random_seed(seed):
torch.manual_seed(seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, default = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0")
parser.add_argument("--refine", action="store_true")
parser.add_argument("--refine_model", type=str, default = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-refiner-1.0")
parser.add_argument("--prompt", type=str, default='a photo of an astronaut on a moon')
parser.add_argument("--seed", type=int, default=42)
args = parser.parse_args()
seed = args.seed
prompt = args.prompt
baseline_pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
args.model, torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16", use_safetensors=True
).to("cuda:0")
if args.refine:
refiner_pipe = StableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
args.refine_model,
text_encoder_2=baseline_pipe.text_encoder_2,
vae=baseline_pipe.vae,
torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True, variant="fp16"
).to("cuda:0")
# Warmup GPU. Only for testing the speed.
logging.info("Warming up GPU...")
for _ in range(0):
set_random_seed(seed)
_ = baseline_pipe(prompt, output_type='pt').images
# Baseline
logging.info("Running baseline...")
start_time = time.time()
set_random_seed(seed)
if args.refine:
image = baseline_pipe(
prompt=prompt,
num_inference_steps=50,
denoising_end=0.8,
output_type="latent",
).images
base_use_time = time.time() - start_time
logging.info("Baseline - Base: {:.2f} seconds".format(base_use_time))
start_time = time.time()
ori_image = refiner_pipe(
prompt=prompt,
num_inference_steps=50,
denoising_start=0.8,
image=image,
output_type="pt"
).images
refine_use_time = time.time() - start_time
logging.info("Baseline - Refiner: {:.2f} seconds".format(refine_use_time))
baseline_use_time = base_use_time + refine_use_time
else:
ori_image = baseline_pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=50, output_type='pt').images
baseline_use_time = time.time() - start_time
logging.info("Baseline: {:.2f} seconds".format(baseline_use_time))
del baseline_pipe
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
# DeepCache
pipe = DeepCacheStableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
args.model, torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16", use_safetensors=True
).to("cuda:0")
if args.refine:
refiner_pipe = DeepCacheStableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-refiner-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True, variant="fp16"
).to("cuda:0")
# Warmup GPU. Only for testing the speed.
logging.info("Warming up GPU...")
for _ in range(1):
set_random_seed(seed)
_ = pipe(
prompt,
cache_interval=3, cache_layer_id=0, cache_block_id=0,
output_type='pt', return_dict=True,
).images
logging.info("Running DeepCache...")
set_random_seed(seed)
start_time = time.time()
if args.refine:
deepcache_base_output = pipe(
prompt,
num_inference_steps=50,
denoising_end=0.8, output_type="latent",
cache_interval=3, cache_layer_id=0, cache_block_id=0,
uniform=True,
return_dict=True
).images
base_use_time = time.time() - start_time
logging.info("DeepCache - Base: {:.2f} seconds".format(base_use_time))
start_time = time.time()
deepcache_output = refiner_pipe(
prompt=prompt,
num_inference_steps=50,
denoising_start=0.8,
cache_interval=3, cache_layer_id=0, cache_block_id=0,
uniform=True,
image=deepcache_base_output,
output_type='pt',
).images
refine_use_time = time.time() - start_time
logging.info("DeepCache - Refiner: {:.2f} seconds".format(refine_use_time))
use_time = base_use_time + refine_use_time
else:
deepcache_output = pipe(
prompt,
num_inference_steps=50,
cache_interval=3, cache_layer_id=0, cache_block_id=0,
uniform=True,
output_type='pt',
return_dict=True
).images
use_time = time.time() - start_time
logging.info("DeepCache: {:.2f} seconds".format(use_time))
logging.info("Baseline: {:.2f} seconds. DeepCache: {:.2f} seconds".format(baseline_use_time, use_time))
save_image([ori_image[0], deepcache_output[0]], "output.png")
logging.info("Saved to output.png. Done!")Deployment
This is your assignment 😁
Here are the endpoints you’ll create
/train/dreambooth: takes in images, and prompt, trains a sdxl dreambooth lora model. returns model-id which can be used to track progress. once model is trained its status is updated to trained in redis and the model is saved in S3, this way you can train hundreds of LoRA’s and load any model at any time.
/status: takes in the model-id and returns the status of training, if its training return the percentage trained with other metadata, like base model, learning rate, vae
/infer/lora: takes in model-id, and text and returns image generated from the model-id trained lora. also it has a parameter for video conversion, if allow_motion parameter is given it returns a video. Instead of returning the video/image as binary object, upload the output to S3, and return a presigned URL instead.
/infer/sdxl: simply runs the normal sdxl model, but optionally has allow_motion parameter
both the /infer endpoints must allow the user to specify one or more lora id’s and also weightage to be given to each lora model. This would allow you to combine outputs from trained trained model with something like pixel lora model
NOTE: you’ll do only one job at a time, i.e. if training is going on, then don’t accept more training jobs or infer jobs
Some hints for speeding up inference
- torch.compile
pipe.unet = torch.compile(pipe.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
pipe.vae = torch.compile(pipe.vae, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)- LCM LoRA
- Loading/Unloading LoRA
- SDXL Turbo (5-10 images per second!) (yes its images/sec not sec/image) (yes this is really that fast)
- 4bit and 8bit inference (https://twitter.com/drawthingsapp/status/1702387777101570199)
NOTES
- SDXL with ControlNet: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1WFpBDoAi3bImpvMCWS-FDwWC2dKtygsx?usp=sharing
- Latent Consistency Model: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1Yc3a5IuKB4lBz5lTlcQ5j2HHrVkE6tqo?usp=sharing
- FuneTuning Diffusion Models with Reinforcement Learning: https://huggingface.co/blog/trl-ddpo
- SDXL Latent Space: https://huggingface.co/blog/TimothyAlexisVass/explaining-the-sdxl-latent-space
- Illustrated Stable Diffusion: https://jalammar.github.io/illustrated-stable-diffusion/
- Loading/Offloading LoRA: https://huggingface.co/blog/lora-adapters-dynamic-loading
- DDPO and TRL Fine Tuning: https://huggingface.co/blog/trl-ddpo